
weathering Kids Britannica Kids Homework Help
weathering, disintegration or alteration of rock in its natural or original position at or near the Earth's surface through physical, chemical, and biological processes induced or modified by wind, water, and climate.

PPT Weathering PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2202343
Biological Weathering By Chemicals/Organic Compounds In this type of weathering, living organisms contribute through organic compounds containing molecules that acidify and corrode rock minerals. Because of such a mechanism, biological weathering is also called organic weathering.

PPT An introduction to coasts PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2795988
Biological weathering is the weakening and subsequent disintegration of rock by plants, animals and microbes. Growing plant roots can exert stress or pressure on rock. Although the process is physical, the pressure is exerted by a biological process ( i. e ., growing roots).

PPT Geomorphic Processes II. Exogenous PowerPoint Presentation ID6334096
Weathering involves physical and chemical processes that are modified by biological activity of plants, microorganisms and animals. This article reviews recent progress made in understanding biological processes contributing to weathering.

How Does Biological Weathering Happen? HubPages
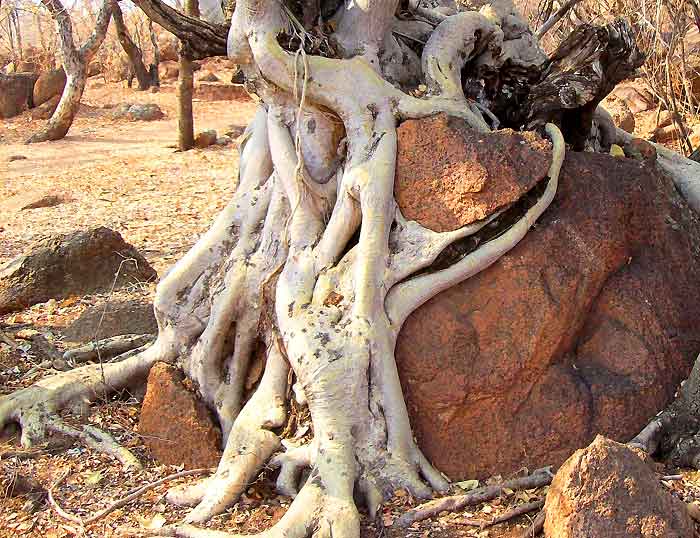
Biological weathering only refers to weathering caused by organisms -- animals, plants, fungi and microorganisms such as bacteria. While certain forms of biological weathering, such as the breaking of rock by tree roots, are sometimes categorized as either physical or chemical, biological weathering can be either physical or chemical.

Freeze Thaw Weathering Geography Wiki Beyond Twinkl
What are the biological processes of weathering? | American Geosciences Institute What are the biological processes of weathering? Living things also help form soil. Once rock is weathered into smaller particles, microorganisms and small plants begin to establish themselves there.

Biological Weathering Definition, Process, Types & Examples
Rock weathering is a key process in global elemental cycling. Life participates in this process with tangible consequences observed from the mineral interface to the planetary scale. Multiple.

Image result for images of rocks expose to elements Chemical weathering, Pressure canning
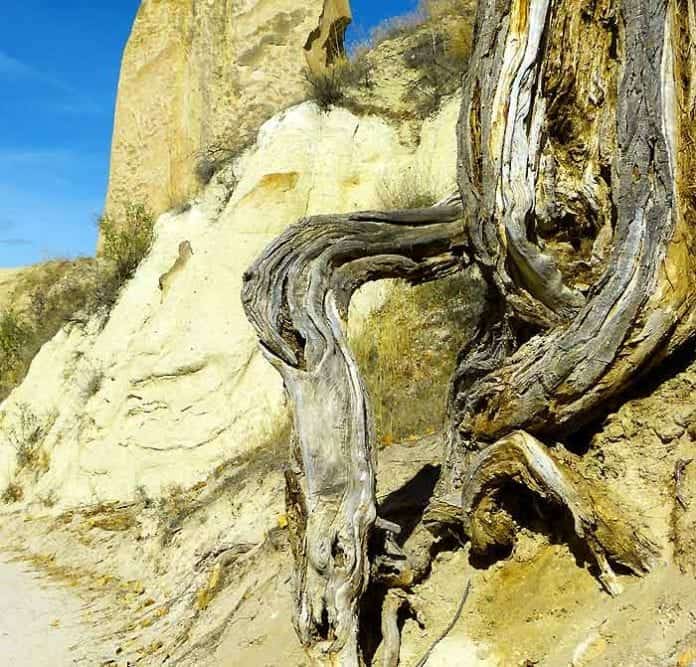
Biological weathering. Plants and animals can also have an effect on rocks. Roots burrow down, weakening the structure of the rock until it breaks away.
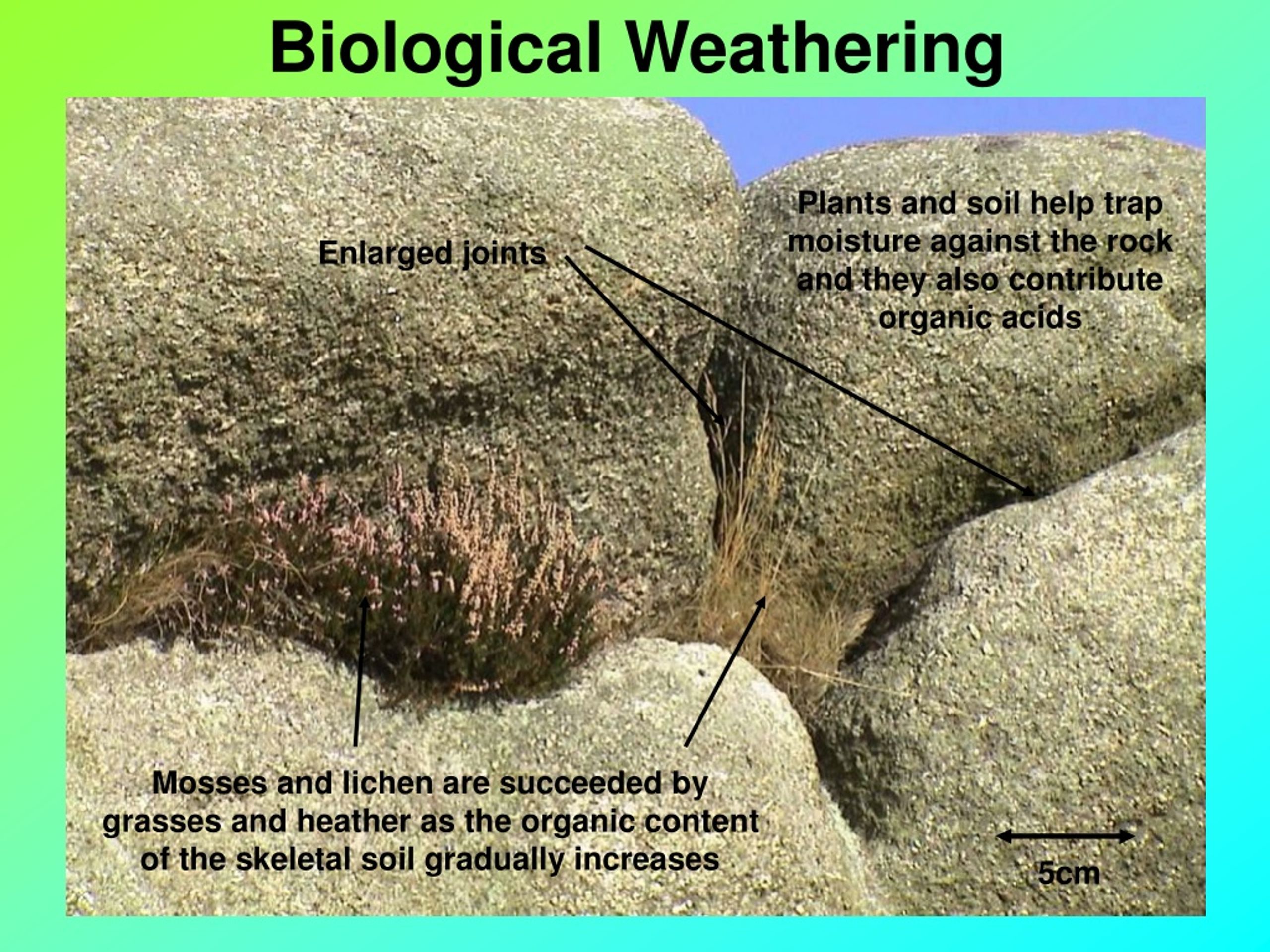
PPT Weathering and the formation of Sedimentary Rocks PowerPoint Presentation ID333327
Biological weathering occurs when plants break up rocks with roots or root exudates. The process is slow, but may strongly influence landscape formation. Biological weathering increases with soil thickness until optima for biotic activity are reached, but decreases when soils get thicker and biotic activity has less influence on weathering.

Weathering Of Rocks Definition DEFINITION HWK
Biological weathering. Biological weathering is caused by the movements of plants and animals. For example, a rabbit can burrow into a crack in a rock making it bigger and eventually splitting the rock, or a plant may grow in a crack in a rock and, as its roots grow, cause the crack to widen. Even you can be a source of weathering!

Biological Weathering Definition, Process, Types & Examples (2022)
The loss of minerals and ions from the environment as a result of the growth or movement of organisms is known as Biological Weathering. It also goes by the name of organic weathering. Animals, bacteria, plants, and people are its primary agents.

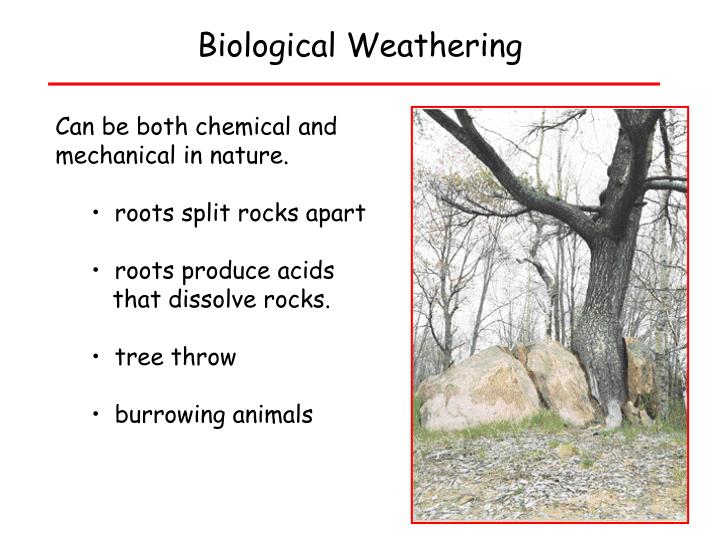
PPT Biological Weathering PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID3034789
Biological weathering, in which living or once-living organisms contribute to weathering, can be a part of both processes. Mechanical Weathering Mechanical weathering, also called physical weathering and disaggregation, causes rocks to crumble. Water, in either liquid or solid form, is often a key agent of mechanical weathering.

What Is Biological Weathering? Sciencing
Organic weathering, also called bioweathering or biological weathering, is the general name for biological processes of weathering that break down rocks. This includes the physical penetration and growth of roots and digging activities of animals ( bioturbation ), as well as the action of lichens and moss on various minerals.

Biological Weathering Definition, Examples, Types, Causes, Agents
Biological Weathering. Biological weathering involves the disintegration of rock and mineral due to the chemical and/or physical agents of an organism. The types of organisms that can cause weathering range from bacteria to plants to animals. Biological weathering involves processes that can be either chemical or physical in character..
/GettyImages-560515091-5982d397d963ac001173b7e4.jpg)
Kuinka kasvit ja eläimet sään aiheuttavat?
Nature's Shapers: Biological weathering is the process by which living organisms - including plants, animals, and microorganisms - contribute to the breakdown of rocks and minerals. Green Warriors: Plant-based weathering occurs when roots penetrate into cracks in rocks, expanding and splitting the rock.
PPT Weathering PowerPoint Presentation ID219934
Chemical weathering by biological action is also known as biological weathering. [3] The materials left over after the rock breaks down combine with organic material to create soil. Many of Earth's landforms and landscapes are the result of weathering processes combined with erosion and re-deposition.